28
Hyponatremia: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments, and the Importance of Sodium
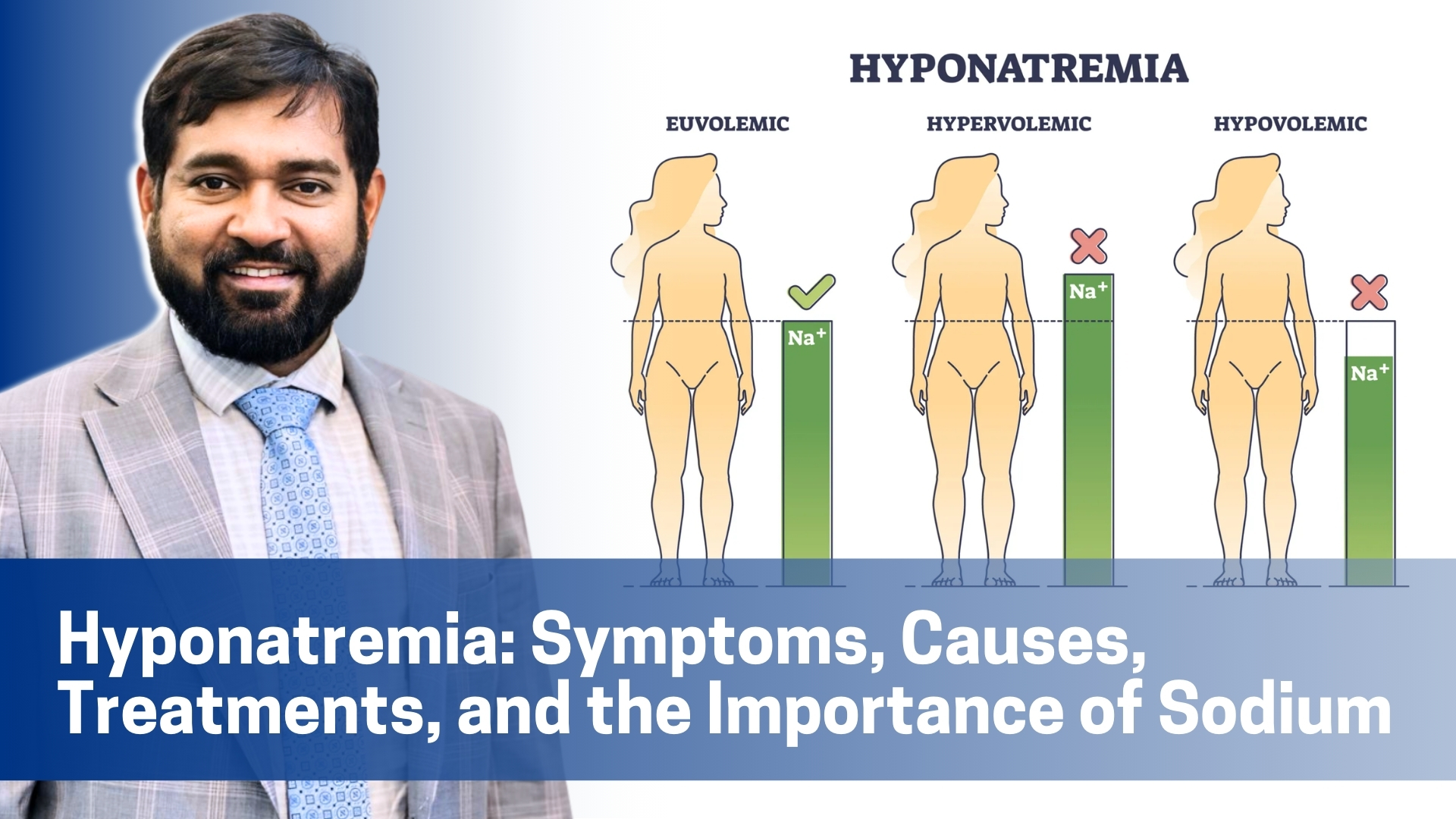
Hyponatremia is a condition characterized by abnormally low sodium levels in the blood, which can lead to various health complications.
Sodium is an essential electrolyte that plays a vital role in maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contraction. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatments, and the overall importance of sodium is crucial for preventing and managing this condition.
What is Hyponatremia?
Hyponatremia occurs when the sodium concentration in the blood falls below the normal range of 135-145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). Sodium helps regulate the balance of water inside and outside cells. When sodium levels drop, water moves into cells, causing them to swell. While this can affect all cells, swelling in brain cells can be particularly dangerous and lead to severe symptoms.
Symptoms of Hyponatremia
The symptoms of hyponatremia vary depending on its severity and how quickly sodium levels drop. Mild cases might go unnoticed, but severe cases can become life-threatening.
-
Mild Symptoms:
- Nausea
- Headache
- Fatigue or low energy
- Muscle weakness or cramps
- Loss of appetite
-
Moderate Symptoms:
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Restlessness
- Coordination issues
-
Severe Symptoms:
- Seizures
- Coma
- Respiratory arrest
- Brain swelling (cerebral edema), which can lead to permanent damage or death
Causes of Hyponatremia
Several factors can lead to low sodium levels, often categorized as dilutional (due to excess water) or depletional (due to sodium loss).
-
Excessive Water Intake:
- Drinking large amounts of water in a short period, especially during endurance events, can dilute sodium levels.
- "Water intoxication" occurs when the kidneys cannot excrete enough water, leading to an imbalance.
-
Conditions Leading to Fluid Retention:
- Heart failure: Fluid retention dilutes sodium levels.
- Liver cirrhosis: Impaired liver function can cause fluid imbalances.
- Kidney diseases: Reduced ability to excrete water effectively.
-
Hormonal Imbalances:
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH): Overproduction of antidiuretic hormone leads to water retention.
- Adrenal insufficiency: Low levels of aldosterone impair sodium reabsorption.
-
Diuretics and Medications:
- Diuretics used for treating high blood pressure or heart failure can increase sodium excretion.
- Certain antidepressants and pain medications can disrupt sodium balance.
-
Loss of Sodium:
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Excessive sweating
- Chronic dehydration
-
Other Causes:
- Severe burns
- Cystic fibrosis
- Use of recreational drugs like MDMA (ecstasy), which is associated with water retention and hyponatremia.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing hyponatremia involves:
- Blood Tests: Measure sodium levels, kidney function, and hormone levels.
- Urine Tests: Check sodium concentration and osmolality to determine if sodium is being lost through the urine.
- Imaging: In cases of suspected brain swelling, CT or MRI scans may be used.
Treatment of Hyponatremia
Treatment varies depending on the severity and underlying cause.
1. Mild Cases
- Fluid Restriction: Limiting water intake can restore the sodium-water balance in cases caused by overhydration.
- Oral Sodium Supplements: Can be used to gradually increase sodium levels.
2. Moderate to Severe Cases
- Intravenous Sodium Solutions: A controlled infusion of hypertonic saline (3% sodium chloride) is administered to quickly raise sodium levels in life-threatening cases.
- Medications:
- Vasopressin receptor antagonists (e.g., tolvaptan) are used in some cases to regulate water excretion without affecting sodium levels.
- Diuretics may help in cases of fluid overload.
- Monitoring: Sodium levels must be corrected slowly to prevent complications like osmotic demyelination syndrome, which can occur if levels are restored too quickly.
3. Addressing Underlying Causes
- Treating hormonal imbalances (e.g., with corticosteroids for adrenal insufficiency).
- Adjusting medications that might contribute to the condition.
- Managing chronic illnesses like heart failure or kidney disease.
Importance of Sodium in the Body
Sodium is essential for various physiological functions:
-
Fluid Balance: Sodium helps maintain the balance of water between cells and their surrounding environment. Proper fluid distribution is crucial for organ function.
-
Nerve Function: Sodium plays a key role in transmitting nerve impulses. It helps generate electrical signals that allow communication between the brain and body.
-
Muscle Contraction: Along with potassium, sodium is vital for muscle contractions. Imbalances can lead to muscle weakness or spasms.
-
Blood Pressure Regulation: Sodium levels influence blood volume and pressure. Low sodium can lead to hypotension, while excessive sodium can cause hypertension.
Preventing Hyponatremia
Prevention involves maintaining a healthy balance of sodium and water in the body:
-
Stay Hydrated (But Not Overhydrated):
- Drink water according to your thirst, especially during exercise. Sports drinks with electrolytes can help replenish sodium lost through sweat.
-
Moderate Sodium Intake:
- While sodium is essential, excessive intake can strain the kidneys and lead to high blood pressure. Aim for a balanced diet.
-
Be Cautious with Medications:
- Use diuretics and other medications as prescribed and discuss side effects with your doctor.
-
Recognize Risk Factors:
- Those with heart failure, liver disease, or other chronic conditions should work with healthcare providers to monitor sodium levels.
-
Seek Early Treatment:
- If symptoms like persistent fatigue, confusion, or muscle weakness occur, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Key Points to Remember
- Hyponatremia Symptoms: Can range from mild fatigue to life-threatening brain swelling.
- Causes: Include excessive water intake, hormonal imbalances, medications, and sodium loss.
- Treatment: Depends on severity but focuses on restoring sodium levels gradually and addressing the underlying cause.
- Sodium's Role: Vital for fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle activity.
- Prevention: Maintain a balanced sodium intake and avoid excessive hydration.
Conclusion
Hyponatremia is a potentially dangerous condition that underscores the importance of sodium in maintaining the body's delicate balance. Understanding its causes and symptoms allows for early detection and prevention. By staying informed, you can make better choices to protect your health and ensure proper hydration. Always consult a healthcare professional if you suspect hyponatremia or experience symptoms associated with low sodium levels.
Here are 15 references about hyponatremia, its symptoms, causes, treatments, and the importance of sodium. Each entry includes a title and a brief description without embedding the links into the text.
-
Hyponatremia Overview - Cleveland Clinic
Discusses causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for hyponatremia.
www.clevelandclinic.org/hyponatremia-overview -
Understanding Low Sodium Levels - Mayo Clinic
Provides a detailed explanation of symptoms, complications, and risk factors associated with hyponatremia.
www.mayoclinic.org/hyponatremia-causes -
Hyponatremia Symptoms and Causes - Johns Hopkins Medicine
Offers insights into conditions leading to low sodium and the physiological effects of the disorder.
www.hopkinsmedicine.org/low-sodium-overview -
Clinical Practice Guidelines on Hyponatremia - European Journal of Endocrinology
Presents a comprehensive guide on diagnosing and treating hyponatremia.
www.eje.org/clinical-hyponatremia -
Sodium Disorders - Merck Manuals
Explores disorders of sodium balance, including hyponatremia, with diagnostic approaches and management.
www.merckmanuals.com/sodium-disorders -
Low Sodium and Brain Function - National Institutes of Health (NIH)
Examines the neurological impact of acute and chronic hyponatremia.
www.nih.gov/brain-health-hyponatremia -
Exercise-Induced Hyponatremia - British Journal of Sports Medicine
Highlights risks of overhydration and sodium loss in athletes.
www.bjsm.org/exercise-hyponatremia -
Hyponatremia: Causes and Management - WebMD
A practical overview of treatment strategies for low sodium levels.
www.webmd.com/hyponatremia-management -
The Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH) - NEJM
Details SIADH as a common cause of hyponatremia and its treatment.
www.nejm.org/siadh-hyponatremia -
Chronic Hyponatremia in Older Adults - PubMed
Discusses age-related factors contributing to chronic hyponatremia.
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/chronic-hyponatremia -
Fluid and Sodium Balance - Kidney Health Australia
Provides information on managing sodium and fluid intake for kidney health.
www.kidney.org.au/sodium-balance -
Acute Hyponatremia - American Journal of Medicine
Explores the critical management of acute hyponatremia and its rapid onset symptoms.
www.amjmed.com/acute-hyponatremia -
Hyponatremia and Water Intake - Medanta
Analyzes the relationship between overhydration and low sodium levels.
www.medanta.org/hyponatremia-overhydration -
Low Sodium Risks and Exercise - Sports Medicine Australia
Describes how excessive water intake during endurance sports can trigger hyponatremia.
www.sma.org/exercise-risks-hyponatremia -
Treatment Guidelines for Hyponatremia - Clinical Endocrinology
Discusses step-by-step approaches to correcting low sodium levels safely.
www.clinendocrinology.com/hyponatremia-treatment